Links:
-
6010% 2RS is a type of deep groove ball bearing, commonly used in a variety of applications. These bearings are known for their high quality and durability, making them a popular choice for many industries. In conclusion, the advantages of tapered roller bearings are multi-faceted, encompassing high load-bearing capacity, adjustability, misalignment tolerance, durability, ease of installation, and high-speed operation. These attributes make them a preferred choice in diverse sectors, from automotive to aerospace, construction to marine. As technology continues to evolve, so does the potential of tapered roller bearings, solidifying their position as a cornerstone in modern engineering. 3. Open bearings These bearings do not have seals and are suitable for applications where the environment is clean and dry.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Cylindrical roller bearings are not designed to accommodate misalignment to the same extent as spherical roller bearings. They are primarily intended for applications where precise shaft positioning and minimal deflection are critical.
Secondly, the complexity of the design and manufacturing process contributes to the pricing. Tapered bearings require precise engineering, with each component - the cones, cups, and rollers - needing to be manufactured to exacting tolerances. This precision engineering, coupled with the need for rigorous quality control, increases the production cost, which is then reflected in the selling price.
Deep groove ball bearings are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including electric motors, pumps, gearboxes, conveyors, and various machinery and equipment. Their ability to handle both radial and axial loads, combined with their low friction and high efficiency, makes them versatile and widely utilized in industrial, automotive, and consumer products.
This innovative bearing boasts a series of enhancements over traditional models. It could feature advanced materials science, employing cutting-edge composites or metal alloys that provide superior strength and resilience. These materials not only extend the bearing's operational lifespan but also improve its load capacity and resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. 4. Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation
Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation Industrial machinery They are employed in industrial machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors to provide reliable and efficient operation miniature deep groove ball bearings. Due to their compact size, high load capacity, and low friction, 627ZZ bearings are widely used in a variety of applications, including The 22214 bearing offers numerous benefits that make it an ideal choice for various applications. Its self-aligning feature allows for misalignment compensation, ensuring smooth operation even in the presence of minor misalignment. The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs
miniature deep groove ball bearings. Due to their compact size, high load capacity, and low friction, 627ZZ bearings are widely used in a variety of applications, including The 22214 bearing offers numerous benefits that make it an ideal choice for various applications. Its self-aligning feature allows for misalignment compensation, ensuring smooth operation even in the presence of minor misalignment. The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs
The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs The high load capacity and rigidity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, while the low friction and heat generation ensure efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance costs 22214 bearing. Additionally, the bearing's ability to accommodate misalignment reduces the risk of premature failure and extends its service life. In conclusion, a deep groove bearing puller is an essential tool for anyone involved in the maintenance of machinery and equipment that uses deep groove bearings. Its ability to quickly and easily remove bearings without damaging them makes it a valuable asset for any workshop or maintenance facility. By investing in a high-quality puller, you can save time, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency of your maintenance operations. In the world of mechanical engineering, precision and performance are paramount, and bearings play a crucial role in ensuring both. The 6314 bearing size, a part of the deep groove ball bearing family, is a widely used component due to its versatility and efficiency. This article delves into the specifics of this bearing size, its dimensions, applications, and the significance it holds in various industries. In conclusion, the LM501349 bearing stands as a symbol of cutting-edge engineering and precision. Its exceptional load-bearing capabilities, low friction design, and durability make it a cornerstone in various industries. As technology continues to advance, the LM501349 bearing remains at the forefront, ensuring smooth motion, reliability, and enhanced efficiency in machinery across the globe. The design elegance of these systems lies in their ability to handle dynamic loads, thanks to the ball bearings’ superior load capacity and uniform contact stresses
22214 bearing. Additionally, the bearing's ability to accommodate misalignment reduces the risk of premature failure and extends its service life. In conclusion, a deep groove bearing puller is an essential tool for anyone involved in the maintenance of machinery and equipment that uses deep groove bearings. Its ability to quickly and easily remove bearings without damaging them makes it a valuable asset for any workshop or maintenance facility. By investing in a high-quality puller, you can save time, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency of your maintenance operations. In the world of mechanical engineering, precision and performance are paramount, and bearings play a crucial role in ensuring both. The 6314 bearing size, a part of the deep groove ball bearing family, is a widely used component due to its versatility and efficiency. This article delves into the specifics of this bearing size, its dimensions, applications, and the significance it holds in various industries. In conclusion, the LM501349 bearing stands as a symbol of cutting-edge engineering and precision. Its exceptional load-bearing capabilities, low friction design, and durability make it a cornerstone in various industries. As technology continues to advance, the LM501349 bearing remains at the forefront, ensuring smooth motion, reliability, and enhanced efficiency in machinery across the globe. The design elegance of these systems lies in their ability to handle dynamic loads, thanks to the ball bearings’ superior load capacity and uniform contact stresses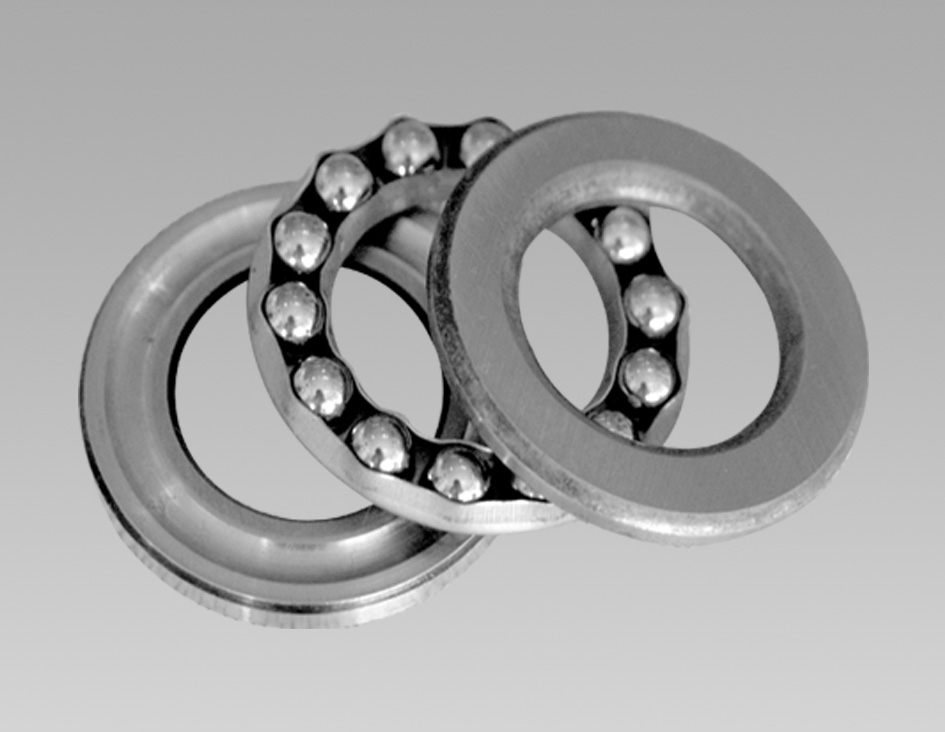 Another significant advantage of four-row taper roller bearings is their ability to accommodate misalignment. In many industrial machines, components are subject to various forms of misalignment, which can cause excessive wear and tear on bearings. Four-row taper roller bearings are specifically designed to tolerate misalignment, ensuring smooth operation and extended bearing life. Stainless thrust bearings are an essential component in various industrial and mechanical applications. These bearings play a crucial role in supporting axial loads in machines with rotating parts, such as turbines, pumps, and gearboxes.
Another significant advantage of four-row taper roller bearings is their ability to accommodate misalignment. In many industrial machines, components are subject to various forms of misalignment, which can cause excessive wear and tear on bearings. Four-row taper roller bearings are specifically designed to tolerate misalignment, ensuring smooth operation and extended bearing life. Stainless thrust bearings are an essential component in various industrial and mechanical applications. These bearings play a crucial role in supporting axial loads in machines with rotating parts, such as turbines, pumps, and gearboxes. Moreover, the L44610 bearing offers exceptional corrosion resistance due to its advanced coating technology
 l44610 bearing. This feature allows it to perform optimally in environments that are exposed to moisture or chemicals, further expanding its range of applications. From marine equipment to chemical processing plants, this bearing proves its mettle in challenging conditions. In conclusion, R8 2RS ball bearings are a versatile and reliable choice for a wide range of applications. Their sealed design, high load capacity, high-speed capability, and precision make them an ideal choice for machinery and equipment used in various industries. By choosing R8 2RS ball bearings for your application, you can ensure smooth and efficient operation of your machinery, leading to improved productivity and reduced downtime. In conclusion, the ball bearing 6203 2RS is a reliable and versatile component that is essential for many machinery applications. Its ability to handle both radial and axial loads, combined with its protective rubber seals, make it a popular choice for various industries. By ensuring proper installation and maintenance, users can maximize the performance and longevity of the bearing, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
l44610 bearing. This feature allows it to perform optimally in environments that are exposed to moisture or chemicals, further expanding its range of applications. From marine equipment to chemical processing plants, this bearing proves its mettle in challenging conditions. In conclusion, R8 2RS ball bearings are a versatile and reliable choice for a wide range of applications. Their sealed design, high load capacity, high-speed capability, and precision make them an ideal choice for machinery and equipment used in various industries. By choosing R8 2RS ball bearings for your application, you can ensure smooth and efficient operation of your machinery, leading to improved productivity and reduced downtime. In conclusion, the ball bearing 6203 2RS is a reliable and versatile component that is essential for many machinery applications. Its ability to handle both radial and axial loads, combined with its protective rubber seals, make it a popular choice for various industries. By ensuring proper installation and maintenance, users can maximize the performance and longevity of the bearing, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs. The deep groove design is particularly advantageous for radial loads, as it enables the bearing to support forces that act perpendicular to the shaft's axis. Additionally, the deep groove configuration allows the bearing to accommodate some degree of axial load, although axial load capacity is typically lower than radial load capacity in deep groove ball bearings.
The Bearing 30x62x21, as the name suggests, refers to a bearing with dimensions of 30 millimeters in inner diameter, 62 millimeters in outer diameter, and 21 millimeters in width. These dimensions are critical as they determine the load capacity, speed rating, and overall performance of the bearing. The 'x' in the name signifies the multiplication of these dimensions, which are crucial for engineers to ensure compatibility with their machinery. Applications of the 51113 Bearing The 32238 bearing finds extensive use in heavy-duty applications such as automotive axles,, wind turbines, and even industrial machinery. Its ability to withstand high radial and axial loads makes it ideal for applications where substantial stress is anticipated. Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions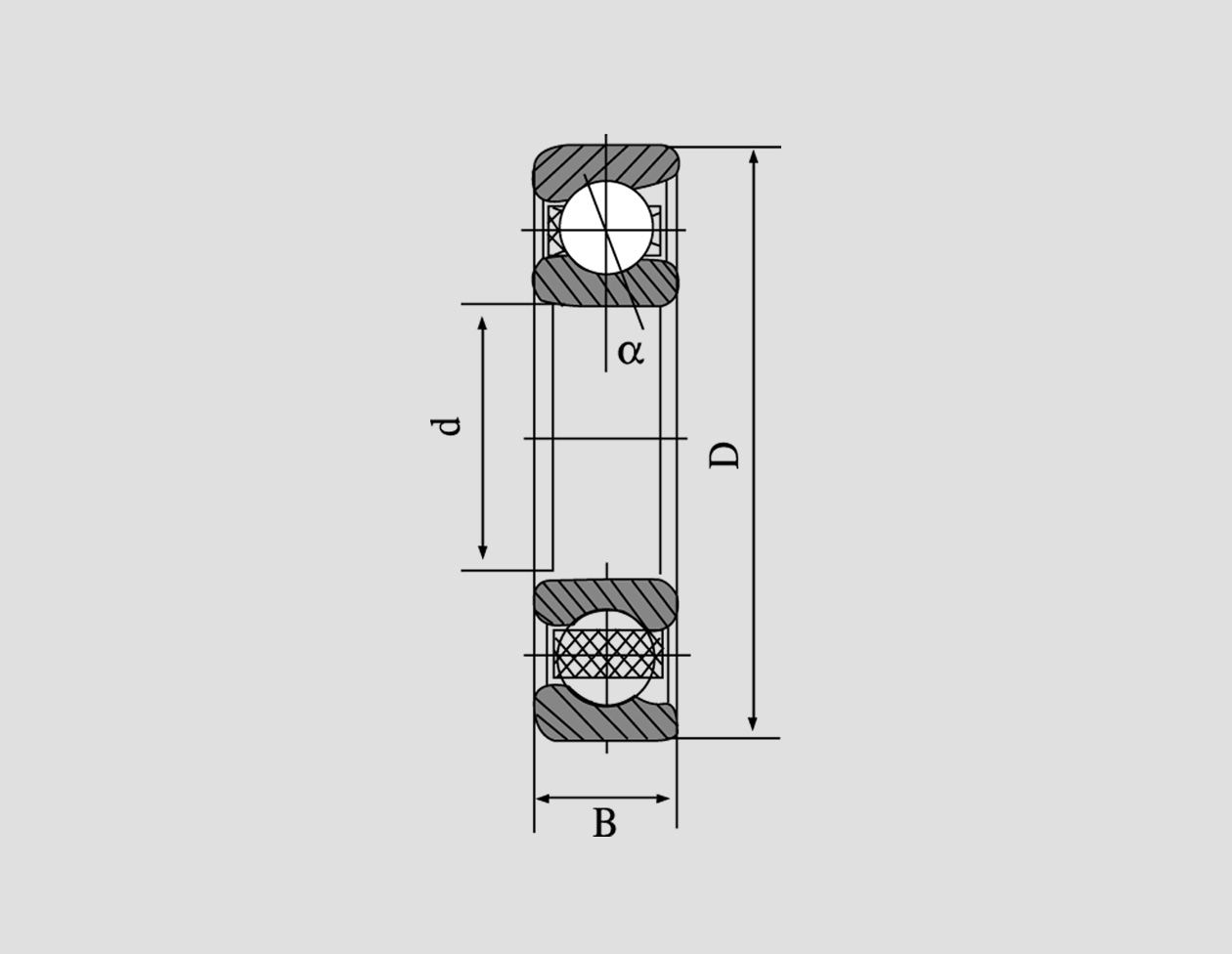 Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions
Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions Moreover, the self-aligning feature of these bearings enables them to accommodate misalignments, making them versatile and adaptable to different operating conditions 32238 bearing. In addition to their strength and durability, cylindrical roller bearings also offer superior stiffness and precision Environmental considerations are also increasingly important in modern industry, and the 6004z bearing aligns well with sustainability efforts Manufacturers often apply heat treatment and surface finishing processes to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of these bearings. Lubrication is another critical factor in maintaining the optimal performance of a tapered roller bearing. Proper lubrication minimizes friction, reduces heat generation, and prolongs the bearing's life. Introduction When discussing the dimensions of 61800 series bearings, it is important to consider several key parameters. The first is the bore diameter, which refers to the inner diameter of the bearing where it fits onto a shaft. This measurement is typically expressed in millimeters and ranges from 10 mm to 16 mm for the 61800 series. It is essential to select a bearing with a bore diameter that matches the shaft size to ensure proper fit and functionality. The 638 ZZ bearing is a versatile and reliable bearing that offers excellent performance in high-speed and heavy-duty applications. Its precision manufacturing, double shields, high load capacity, low friction, and long service life make it an ideal choice for a wide range of industries. By understanding the features, specifications, and applications of the 638 ZZ bearing, users can select the appropriate bearing for their specific needs and ensure optimal performance and reliability. In conclusion, the 32213 bearing is a versatile and reliable component that plays a crucial role in many industrial applications. Its tapered roller design, durability, and ease of installation make it a popular choice for equipment manufacturers and maintenance professionals looking for high-performance bearings. By choosing the 32213 bearing, engineers and technicians can ensure smooth and efficient operation of their machinery, leading to improved performance and reduced maintenance costs. Double row cylindrical roller bearings, as the name suggests, have two rows of rollers, providing double the load capacity compared to single row bearings. They can handle both radial and certain axial loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery like turbines and compressors. Their design allows for self-aligning capabilities, compensating for slight misalignments. In addition to these functional advantages, tapered roller bearings also offer benefits in terms of maintenance and cost-effectiveness. Their replaceable components, including the cones, cups, and rollers, allow for partial replacements instead of the entire bearing, reducing downtime and overall maintenance costs. The versatility of the 51204 bearing makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in automotive components, such as transmissions, differentials, and wheel hubs. In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans
32238 bearing. In addition to their strength and durability, cylindrical roller bearings also offer superior stiffness and precision Environmental considerations are also increasingly important in modern industry, and the 6004z bearing aligns well with sustainability efforts Manufacturers often apply heat treatment and surface finishing processes to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of these bearings. Lubrication is another critical factor in maintaining the optimal performance of a tapered roller bearing. Proper lubrication minimizes friction, reduces heat generation, and prolongs the bearing's life. Introduction When discussing the dimensions of 61800 series bearings, it is important to consider several key parameters. The first is the bore diameter, which refers to the inner diameter of the bearing where it fits onto a shaft. This measurement is typically expressed in millimeters and ranges from 10 mm to 16 mm for the 61800 series. It is essential to select a bearing with a bore diameter that matches the shaft size to ensure proper fit and functionality. The 638 ZZ bearing is a versatile and reliable bearing that offers excellent performance in high-speed and heavy-duty applications. Its precision manufacturing, double shields, high load capacity, low friction, and long service life make it an ideal choice for a wide range of industries. By understanding the features, specifications, and applications of the 638 ZZ bearing, users can select the appropriate bearing for their specific needs and ensure optimal performance and reliability. In conclusion, the 32213 bearing is a versatile and reliable component that plays a crucial role in many industrial applications. Its tapered roller design, durability, and ease of installation make it a popular choice for equipment manufacturers and maintenance professionals looking for high-performance bearings. By choosing the 32213 bearing, engineers and technicians can ensure smooth and efficient operation of their machinery, leading to improved performance and reduced maintenance costs. Double row cylindrical roller bearings, as the name suggests, have two rows of rollers, providing double the load capacity compared to single row bearings. They can handle both radial and certain axial loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery like turbines and compressors. Their design allows for self-aligning capabilities, compensating for slight misalignments. In addition to these functional advantages, tapered roller bearings also offer benefits in terms of maintenance and cost-effectiveness. Their replaceable components, including the cones, cups, and rollers, allow for partial replacements instead of the entire bearing, reducing downtime and overall maintenance costs. The versatility of the 51204 bearing makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in automotive components, such as transmissions, differentials, and wheel hubs. In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans
In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans In industrial machinery, it can be found in conveyors, pumps, and fans 51204 bearing. The bearing's durability and reliability also make it ideal for use in aerospace and defense systems. Considerations for Using Low-Price Bearings The inner diameter of the 62201 bearing is 10mm, which is the distance between the center point of the inner ring and the center point of the outer ring. This dimension determines the size of the shaft that can be mounted on the bearing. The outer diameter of the bearing is 32mm, which is the distance between the two rings of the bearing. This dimension affects the overall size of the assembly and the space available for other components. Taper Roller Bearings Precision and Efficiency in Motion Control The 6300 series ball bearings come in various sizes, with inner diameters ranging from 10mm to 40mm and outer diameters ranging from 30mm to 80mm. The width of the bearings varies depending on the size, but typically ranges from 9mm to 26mm. The basic load ratings for these bearings range from 7.8kN to 35.2kN, while the dynamic load ratings range from 15.6kN to 706kN to 70
51204 bearing. The bearing's durability and reliability also make it ideal for use in aerospace and defense systems. Considerations for Using Low-Price Bearings The inner diameter of the 62201 bearing is 10mm, which is the distance between the center point of the inner ring and the center point of the outer ring. This dimension determines the size of the shaft that can be mounted on the bearing. The outer diameter of the bearing is 32mm, which is the distance between the two rings of the bearing. This dimension affects the overall size of the assembly and the space available for other components. Taper Roller Bearings Precision and Efficiency in Motion Control The 6300 series ball bearings come in various sizes, with inner diameters ranging from 10mm to 40mm and outer diameters ranging from 30mm to 80mm. The width of the bearings varies depending on the size, but typically ranges from 9mm to 26mm. The basic load ratings for these bearings range from 7.8kN to 35.2kN, while the dynamic load ratings range from 15.6kN to 706kN to 70 6kN to 706kN to 70
6kN to 706kN to 70 ball bearing 6300.4kN. The temperature range for these bearings is -30°C to +120°C. The Impact of Bearing 32010X on Modern Industry Furthermore, the 6301 diameter bearing is relatively easy to maintain. Its simple design and readily available replacement parts make it a cost-effective solution for long-term use. With proper care and regular inspection, this bearing can provide years of reliable service, making it a sound investment for any business or project. In addition to efficiency gains, cylindrical thrust bearings offer enhanced performance in high-load situations. Their robust design makes them suitable for heavy-duty operations where other types of bearings might fail due to excessive force concentrations. For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly
ball bearing 6300.4kN. The temperature range for these bearings is -30°C to +120°C. The Impact of Bearing 32010X on Modern Industry Furthermore, the 6301 diameter bearing is relatively easy to maintain. Its simple design and readily available replacement parts make it a cost-effective solution for long-term use. With proper care and regular inspection, this bearing can provide years of reliable service, making it a sound investment for any business or project. In addition to efficiency gains, cylindrical thrust bearings offer enhanced performance in high-load situations. Their robust design makes them suitable for heavy-duty operations where other types of bearings might fail due to excessive force concentrations. For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly
For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly For instance, in wind turbines, where the rotor blades generate significant thrust during operation, these bearings ensure stable rotation and prevent potential damage to the turbine assembly cylindrical thrust bearing. 6307 Bearing The Ultimate Solution for High-Performance Machinery
cylindrical thrust bearing. 6307 Bearing The Ultimate Solution for High-Performance Machinery - Radial contact bearings, also known as deep groove ball bearings, are designed primarily to support radial loads, which are forces acting perpendicular to the shaft's axis.
Specifications of Ball Bearing 6004 2RS In conclusion, the 6207 2RS is not just a string of alphanumeric characters but represents a highly-engineered component that plays a crucial role in the seamless operation of countless machines. Its combination of durability, precision, and sealing technology underscores the importance of quality bearings in modern engineering. Whether it's a high-speed motor or a heavy-duty machinery, the 6207 2RS stands as a testament to the power of engineering innovation and its impact on our daily lives. Size Chart of Double Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings The significance of 6300 2rsr becomes clear when we consider the historical context in which it was first introduced

