Links:
-
This modification results in a more hydrophilic polymer compared to unmodified cellulose, which significantly enhances its solubility in water. The hydroxyethyl substituents disrupt the strong hydrogen bonding between cellulose chains, reducing the overall crystallinity and making the polymer more accessible to water molecules. As a result, HEC readily dissolves in cold water, forming viscous solutions that exhibit pseudoplastic behavior—they flow easily when stirred but become thicker when left to stand. When looking for hydroxyethylcellulose for sale, it's crucial to choose a reputable supplier that ensures high-quality products, meeting industry standards and specifications. The availability of HEC in different grades caters to the diverse needs of various applications, ranging from low viscosity grades for thinning liquids to high viscosity ones for thickening purposes. HPMC is also commonly found in food products as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier

hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose cas no. Its inert nature makes it safe for consumption and it is commonly used in dairy products, sauces, and desserts to improve texture and consistency. In addition, HPMC is used in gluten-free baking to replicate the structural properties of gluten in doughs and batters.
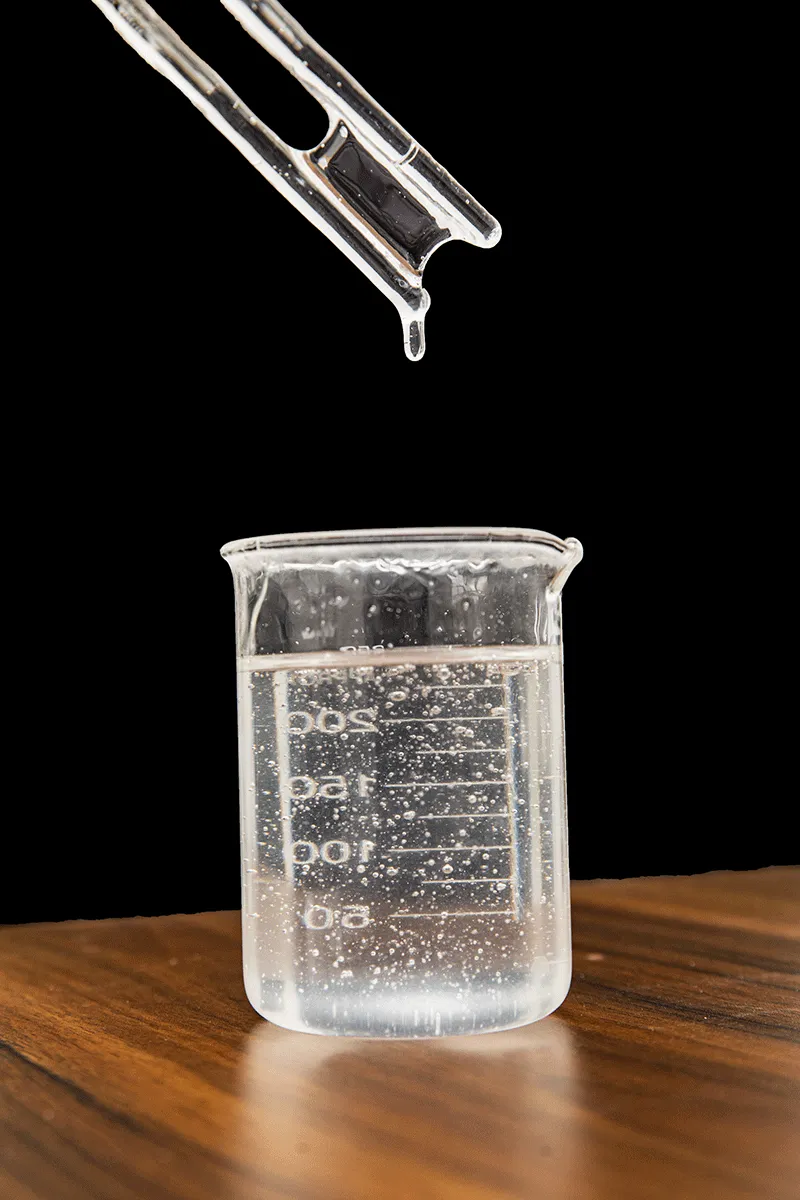
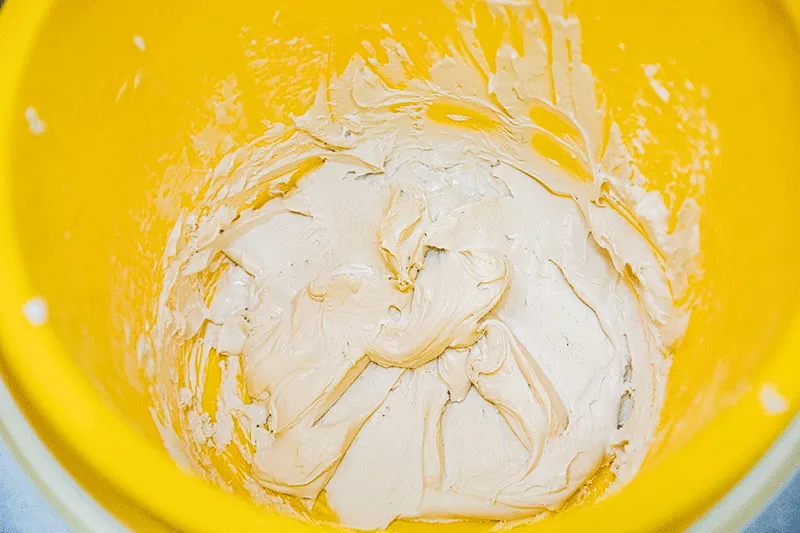



 hpmc dispersion. A well-dispersed HPMC solution should exhibit consistent viscosity over time, be free from visible particles, and have minimal settling. The right balance of HPMC concentration, hydration temperature, and mixing conditions can optimize these properties. In the ever-evolving landscape of materials science, the advent of RDP Polymer marks a significant milestone. This innovative material, with its unique properties and wide-ranging applications, is set to revolutionize various industries, from biomedical to electronics. In recent years, we've seen a significant uptick in the demand for redispersible polymer powders across the globe. This surge can be attributed to the growing construction sector, especially in Asia Pacific and Middle East regions. As urbanization accelerates, so does the need for high-quality building materials that ensure durability and sustainability. Moreover, HEC is a key ingredient in food products, primarily used as a food gum to modify texture and improve mouthfeel. It is also used as a fat substitute, contributing to the development of low-fat and low-calorie products. In conclusion, the price of HPMC is a reflection of a dynamic interplay between raw material costs, production expenses, market demand, geopolitical factors, industry trends, and company strategies. As such, monitoring these factors is crucial for businesses relying on HPMC to make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with price fluctuations.
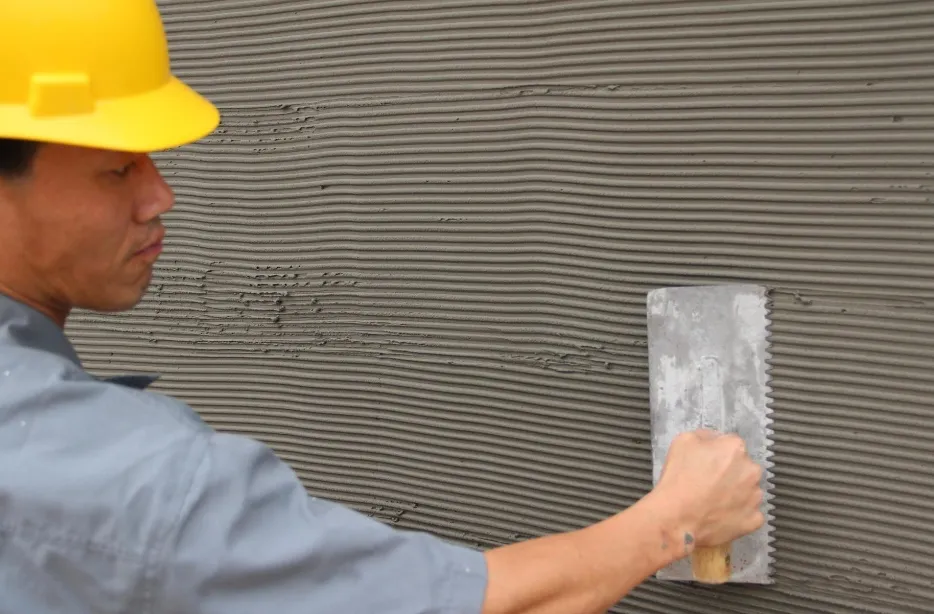
hpmc dispersion. A well-dispersed HPMC solution should exhibit consistent viscosity over time, be free from visible particles, and have minimal settling. The right balance of HPMC concentration, hydration temperature, and mixing conditions can optimize these properties. In the ever-evolving landscape of materials science, the advent of RDP Polymer marks a significant milestone. This innovative material, with its unique properties and wide-ranging applications, is set to revolutionize various industries, from biomedical to electronics. In recent years, we've seen a significant uptick in the demand for redispersible polymer powders across the globe. This surge can be attributed to the growing construction sector, especially in Asia Pacific and Middle East regions. As urbanization accelerates, so does the need for high-quality building materials that ensure durability and sustainability. Moreover, HEC is a key ingredient in food products, primarily used as a food gum to modify texture and improve mouthfeel. It is also used as a fat substitute, contributing to the development of low-fat and low-calorie products. In conclusion, the price of HPMC is a reflection of a dynamic interplay between raw material costs, production expenses, market demand, geopolitical factors, industry trends, and company strategies. As such, monitoring these factors is crucial for businesses relying on HPMC to make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with price fluctuations.  hpmc for putty powder. Generally, a lower percentage is sufficient for basic applications, while higher percentages may be needed for more demanding tasks that require superior adhesion and durability. The precise ratio needs to be determined through careful experimentation and testing, balancing the desired properties with cost-effectiveness. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a widely used substance across various industries due to its versatile properties and non-toxic nature. The question of whether HPMC is safe, however, is one that often arises, particularly in the context of its application in food, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials.
hpmc for putty powder. Generally, a lower percentage is sufficient for basic applications, while higher percentages may be needed for more demanding tasks that require superior adhesion and durability. The precise ratio needs to be determined through careful experimentation and testing, balancing the desired properties with cost-effectiveness. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a widely used substance across various industries due to its versatile properties and non-toxic nature. The question of whether HPMC is safe, however, is one that often arises, particularly in the context of its application in food, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials. 